< Key Hightlight >
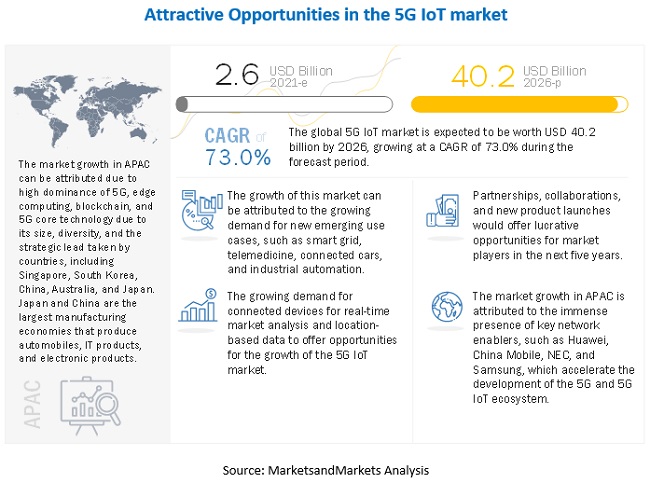
The global 5G IoT market size is expected to grow from USD 2.6 billion in 2021 to USD 40.2 billion by 2026, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 73.0% during the forecast period. Due to the speed, massive capacity, and super low latency of the 5G network, 5G is expected to be the strongest enabler in the expansion of the IoT. The 5G network has the capability to support a massive number of static and mobile IoT devices, having a diverse range of speed, bandwidth, and quality of service requirements. The unprecedented speed, large bandwidth, low latency, massive scalability, and high reliability of the 5G network suit applications, such as consumer VR/AR, AI, and autonomous vehicles, with high data density and rapid response requirements, thus enabling faster adoption of these technologies. Countries expected to launch 5G services at the earliest include the US, China, South Korea, Japan, the UK, and Germany. Countries with a strong 4G infrastructure are expected to be the early deployers Countries with agile connectivity platforms in IoT are also expected to quickly transform their services into 5G, probably by 2020 Q1.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected every segment of society, including individuals and businesses. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the telecom sector is playing a vital role across the globe to support the digital infrastructure of countries. Every individual and government, irrespective of federal, state, central, local, and provinces, has been in constant touch with one other in the society to provide and get real-time information on COVID-19. Currently, healthcare, telecommunication, media and entertainment, utilities, and government institutes are functioning day and night to stabilize the condition and facilitate prerequisite services to every individual.
COVID-19 cases are growing day-by-day, as several infected cases have been on the rise. In line with individuals, COVID-19 has a massive impact on large enterprises and SMEs. Core industries, such as manufacturing, automotive, textile, transportation and logistics, travel and hospitality, and consumer goods, have been closed due to country-level lockdown across the globe. This would have a substantial impact on the global economy in terms of the decline in GDP. Since ages, SMEs are acting as the backbone of the economy. In the current situation, SMEs are the most affected due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Market Dynamics
Driver: Development of Wireless Technologies
IoT devices are connected using a wide variety of wireless technologies, and these technologies offer different benefits and use cases. The increasing adoption of LPWAN, Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN), 5G, wireless sensor networks, and Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is expected to drive the demand for IoT devices, which would increase the requirement of wireless technologies over the next two years. With the increased data exchange rate among large numbers of connected devices, the need to provide increased capacity, high data rate, and high connectivity has also increased. Thus, 5G wireless networks are considered as a key driver for IoT as 5G supports low-latency use cases at the network edge, thereby enabling Communication Service Providers (CSPs) and enterprises to connect mobile and IoT devices, data centers, and public or private cloud platforms. The evolution of Long-Term Evolution (LTE) to 5G is expected to gain pace to support these requirements of emerging IoT applications categorized as massive machine-type communication and mission-critical applications.
Restraint: Lack of standardization in IoT protocol
As a diverse range of devices needs to be connected, the need to coordinate with these different devices has increased. Various devices use different hardware, run over different platforms, and are manufactured by different vendors. This incompatibility among devices, sensors, and even interfaces of remote servers causes the interoperability challenge in the IoT space. IoT involves every aspect of human life, and the challenge lies in unifying these standards so that M2M communication becomes user-friendly and flexible. Several associations and organizations are working toward resolving this issue. The existing interoperability standards, such as MTConnect, Ethernet for Control Automation Technology (EtherCAT), MCS-DCS Interface Standardization (MDIS), Master Control System (MCS), Distributed Control System(DCS), and Interface Standardization, promote data interchange across heterogeneous domains and industries. Companies are currently using custom Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and solutions for every IoT project. A common protocol and communication standard is required to enable communication among IoT-enabled devices to share data or form an intelligent network.
Opportunity: Demand for Private 5G network across enterprises, governments, and industries
Private 5G networks are local area networks that utilize the 5G technology as their communication medium to build private networks. These networks are referred to as local 5G networks or Mobile Private Networks (MPNs) and offer unified connectivity with numerous advantages and optimized services. In the near future, these networks are expected to become one of the preferred choices. They would provide next-generation connectivity for business applications, such as autonomous vehicles, connected factories, connected healthcare, smart retail, and rural broadband connectivity. All these use cases require low latency and higher throughput along with greater precision. The private 5G networks use 5G non-standalone and standalone architectures with license and unlicensed bands specifically designed for highly mission-critical business applications. These networks would use a network slicing technique that helps enterprises utilize resources. North America and Europe have shown a positive approach toward deploying the private 5G networks.
Challenge: Risk of uncertainty in terms of RoIs
Enterprises consider 5G as an enabler of their evolving IoT agendas. IoT improves the effectiveness of enterprise operations and ensures proper asset usage, extends equipment service life, improves reliability, and provides improved return on assets. However, IoT deployments in various industries incur several huge initial investments, such as spending on hardware (sensors and gateways), connectivity, cloud storage, administrative labor, and technical support. There is uncertainty related to Return on Investments (RoIs), and thus, businesses have to consider how quickly they can introduce new solutions and how fast it would take for a solution to start generating revenue. Therefore, in various countries, SMEs do not get easily ready to incur such huge initial costs of IoT deployment, which can hinder the market growth. 5G network deployments are in the introductory stage of product life cycle, with standalone solutions transitions requires efforts. 5G networks can provide advantages, such as Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS) and network slicing. Operators need end-to-end 5G networks to be expansible and flexible so that they can efficiently deliver extensive services to users, which finally brings competitive advantages to operators.
Among network type, 5G Standalone architecture segment to grow at the higher CAGR during the forecast period
5G NR SA is a completely new radio network for 5G networks. It mainly comprises 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) and 5G core networks. 5G NR SA solutions are expected to be more effective than 5G NR NSA solutions. The 5G NR SA solutions have various new built-in capabilities. Some of the new built-in capabilities are network slicing, ultra-low latency, Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS), multi-Gbps support, and virtualization. The 5G NR SA segment is at a nascent stage. It is expected to grow exponentially during the forecast period. In June 2018, 3GPP approved specifications for 5G NR SA. This announcement has accelerated the deployment of 5G network services over a standalone architecture. The standalone architecture offers various benefits, including high performance, greater flexibility, and less complexity.
Among end user, the manufacturing segment is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period
Based on end user, the manufacturing segment of the 5G IoT market is projected to hold a larger market size during the forecast period. With Industry 4.0 underway, the introduction of 5G has accelerated the development of Intelligent factories of the future with its high capacity, wireless flexibility, and low-latency performance capabilities. Manufacturers are embracing digitalization for curbing costs and improving ROI, and 5G IoT assures new process efficiencies and cutting-edge technological advancements, thereby increasing profitability and shop floor productivity. Industry 4.0 is expected to be fueled by cyber-physical systems and IoT, which would require the support of 5G networks. This would enable efficient, connected, and flexible factories of the future. Inside factories, 5G would facilitate manufacturing procedures, such as more efficient production lines (with machine vision and high-definition videos for managing processes), AGVs in factories (autonomous transportation), and machine control with less than 5ms latency using URLLC. Manufacturing organizations are increasingly deploying IoT solutions to connect various functions of the value chain for integrating their business operations. The 5G smart factory of the future promises to create a fully connected experience, thus helping manufacturing companies in realizing major benefits such as performance improvements, operational efficiencies, and increased safety.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
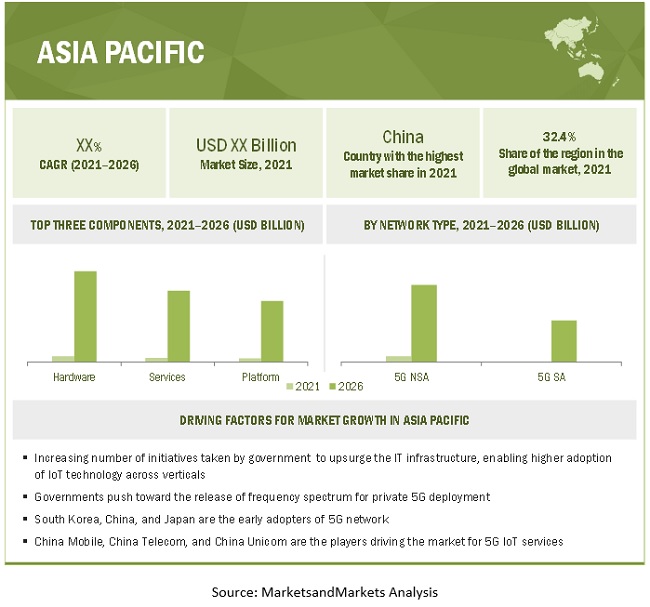
APAC to account for the largest market size during the forecast period
APAC is estimated to hold the largest market share in 2021. The region is transforming dynamically with respect to the adoption of new technologies across various sectors. The infrastructural growth in APAC, especially in Japan, South Korea, Australia, Singapore, China, and India, and the increasing deployment of 4G and 5G networks present huge opportunities for the implementation of the 5G IoT services. Due to a massive mobile subscriber base, enterprises in this region are becoming more competitive and focusing on offering better customer service. The region is set to dominate 5G, edge computing, blockchain, and 5G core technology, due to its size, diversity, and the strategic lead taken by countries, including Singapore, South Korea, China, Australia, and Japan.
Market Players
The report includes the study of key players offering 5G IoT. It profiles major vendors in the global 5G IoT market. The major vendors include China Mobile (China), AT&T (US), Verizon (US), T-Mobile (US), Vodafone (UK), Orange S.A (France), Telefonica (Spain), SK Telecom (South Korea), Deutsche Telekom (Germany),Ericsson(Sweden), Huawei(China), Nokia(Finland), Samsung (South Korea), Cisco(US),NEC(Japan), Sierra Wireless (Canada), Thales(France), Telit(UK), Quectel(China), SIMCom(China), GosuncnWelink(China), Neoway(China), Fibocom(China), u-blox(Switzerland), and Sequans(France).These players have adopted various strategies to grow in the global 5G IoT market.
The study includes an in-depth competitive analysis of these key players in the 5G IoT market with their company profiles, recent developments, and key market strategies.
Scope of Report
Report Metric | Details |
Market size available for years | 2020-2026 |
Base year considered | 2020 |
Forecast period | 2021-2026 |
Forecast units | Value (USD Million) |
Segments covered | components (hardware, platform, connectivity, and services), network type, end user, and regions |
Regions covered | North America, Europe, APAC, and RoW |
Companies covered | China Mobile (China), AT&T (US), Verizon (US), T-Mobile (US), Vodafone (UK), Orange S.A (France), Telefonica (Spain), SK Telecom (South Korea), Deutsche Telekom (Germany),Ericsson(Sweden), Huawei(China), Nokia(Finland), Samsung (South Korea), Cisco(US),NEC(Japan), Sierra Wireless (Canada), Thales(France), Telit(UK), Quectel(China), SIMCom(China), GosuncnWelink(China), Neoway(China), Fibocom(China), u-blox(Switzerland), and Sequans(France). |
This research report categorizes the 5G IoT market to forecast revenue and analyze trends in each of the following submarkets:
Based on Components
- Hardware
- Platform
- Connectivity
- Services
- Professional Services
- Managed Services
Based on Network Type:
- 5G Standalone (SA)
- 5G Non-standalone (NSA)
Based on End user:
- Manufacturing
- Healthcare
- Energy and Utilities
- Automotive and Transportation
- Supply Chain and Logistics
- Government and Public Safety
- Agriculture
- Others End Users (Retail, Smart Building, and Education)
Based on regions:
- North America
- Europe
- APAC
- RoW
Recent Developments:
- In January 2021,AT&T launched its 5G+ services in some popular areas and venues across Tampa, such as Channel District, Raymond James stadium, and Tampa International Airport in the US.
- In November 2021, CMIoT is a subsidiary of China Mobile Communications Group, introduced IoT OS called OneOS that supports 5G network standards. It has characteristics such as cross-platform, scalable, low energy consumption, and high safety.
- In February 2021, Verizon partnered with Zyter, one of the leading digital health and IoT-enablement platform providers, to aid sports and entertainment venues with 5G experiences.
- In November 2020,Ericsson completed the acquisition of Cradlepoint, one of the innovative vendors in WLAN, edge, and IoT solutions. Cradlepoint helps businesses to connect edge devices, vehicles, mobile sites, workforce, and IoT devices.
- In December 2020, Huawei and SIACAS collaborated to introduce their ‘5G+Industrial Network’ joint innovation center. 5G+Industrial Network’ is crucial for Industry 4.0, and improves network connectivity and stability, building a new architecture for industrial interconnections. It provides back-up for next-generation fully connected smart factories
- In June 2020,Vodafone, together with Ford, developed the potential of 5G in manufacturing. Vodafone would deliver a 5G mobile private network by installing Electrified Powertrain in the Manufacturing Engineering (E:PriME) facility on Ford’s Dunton Camp. Vodafone’s 5G connectivity would speed up the manufacturing of electric vehicles for Ford.
Key Benefits of Buying the Report
The report would provide the market leaders/new entrants in this market with information on the closest approximations of the revenue numbers for the overall 5G IoT market and its subsegments. It would help stakeholders understand the competitive landscape and gain more insights better to position their business and plan suitable go-to-market strategies. It also helps stakeholders understand the pulse of the market and provides them with information on key market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities.




